![Rectangle]()
Dive into the Companion Planting Chart: Key Plant Pairings
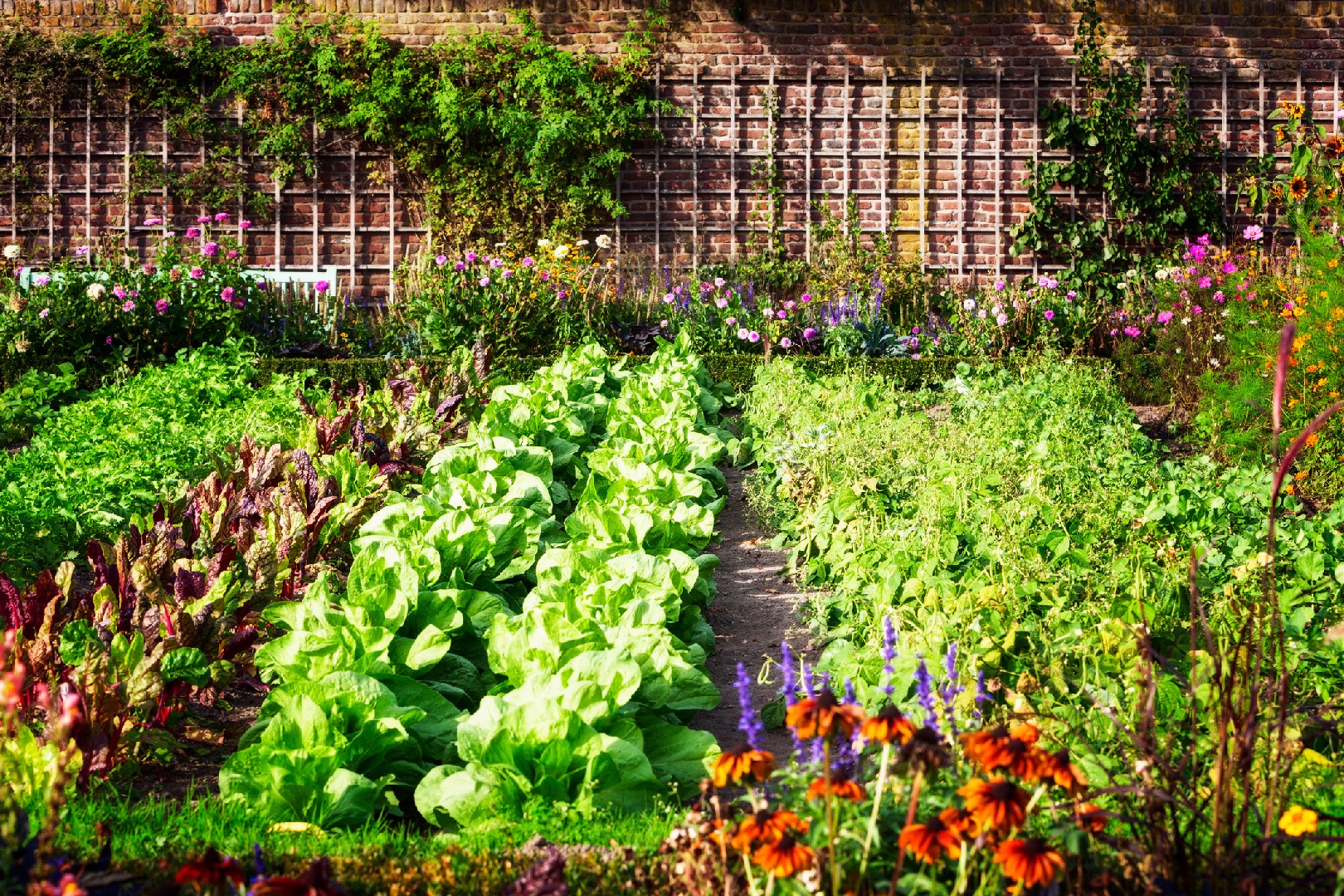
Companion planting is an art that can greatly benefit your garden. By strategically placing plants that have beneficial relationships, you can maximize growth, improve soil health, and deter pests. In this section, we will explore common plant pairs and explain why they are beneficial companions.
One popular example of companion plants is the combination of tomatoes and basil. Tomatoes repel pests such as aphids, while basil enhances the flavor of tomatoes and improves their growth. By planting these two together, you not only improve the health of both plants, but you also have a delicious harvest to look forward to.
Another well-known pair is carrots and onions. Onions help repel carrot flies, while carrots help mask the scent of onions, preventing them from attracting onion flies. This combination is not only beneficial for pest control but also enhances the flavor of both vegetables when cooked together.
When it comes to herbs, rosemary and sage make great companions. Rosemary repels pests such as cabbage moths, while sage attracts beneficial insects like bees and butterflies. Planting these two herbs together creates a natural pest control system while also attracting pollinators to your garden.
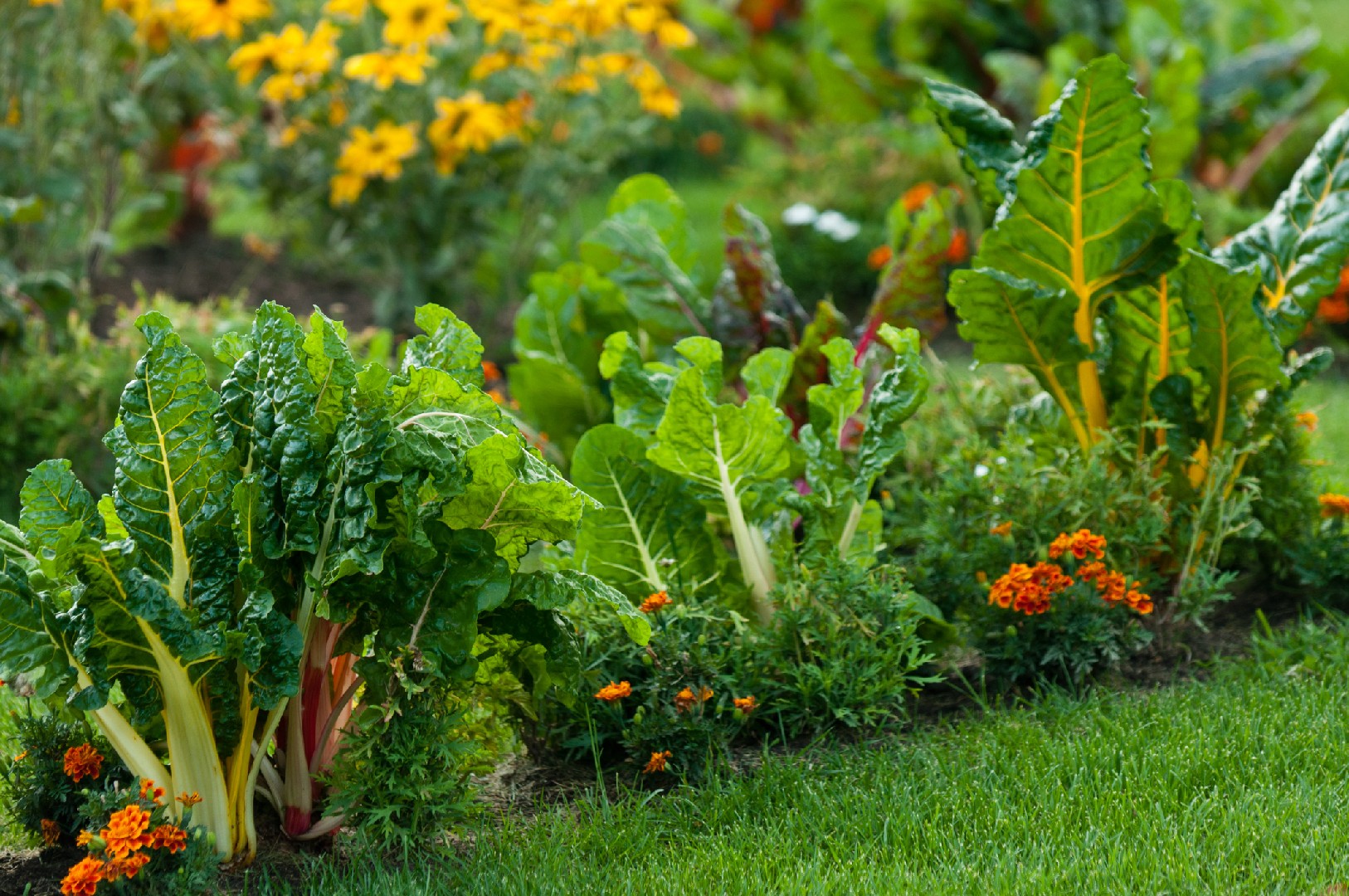
While there are many common plant pairs, it's important to note that different types of edible plants have different companion planting variations. For vegetables, some other beneficial combinations include lettuce and radishes, beans and corn, and cucumbers and sunflowers.
For herbs, consider planting dill and fennel together. Dill attracts beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, while fennel attracts hoverflies and wasps. Together, they create a diverse ecosystem that can naturally control pests in your herb garden.
Fruits also have their own companion planting combinations. One example is planting strawberries and spinach together. Spinach acts as a living mulch, providing shade and moisture to the strawberries, while the strawberries suppress weeds around the spinach.
While companion planting offers many benefits, there are also some pitfalls to watch out for. Some plants are not compatible and can hinder each other's growth. For example, avoid planting onions near beans, as onions can stunt the growth of beans. Additionally, certain crops, such as tomatoes and potatoes, should not be planted together as they are both susceptible to similar diseases like late blight.
In conclusion, the companion planting chart provides a valuable resource for gardeners looking to maximize their plant's potential. By understanding and utilizing key plant pairings, you can create a harmonious and thriving garden. Experiment with different combinations, keeping in mind the variations for different types of edible plants, and always be mindful of incompatible pairings. Happy gardening!